Articles relating to "Press Metalforming Basics."

Presses form products by exerting the necessary load on material via the dies. If the load is not transmitted appropriately, it can result in defective products and cause die damage. In this ...
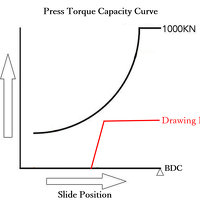
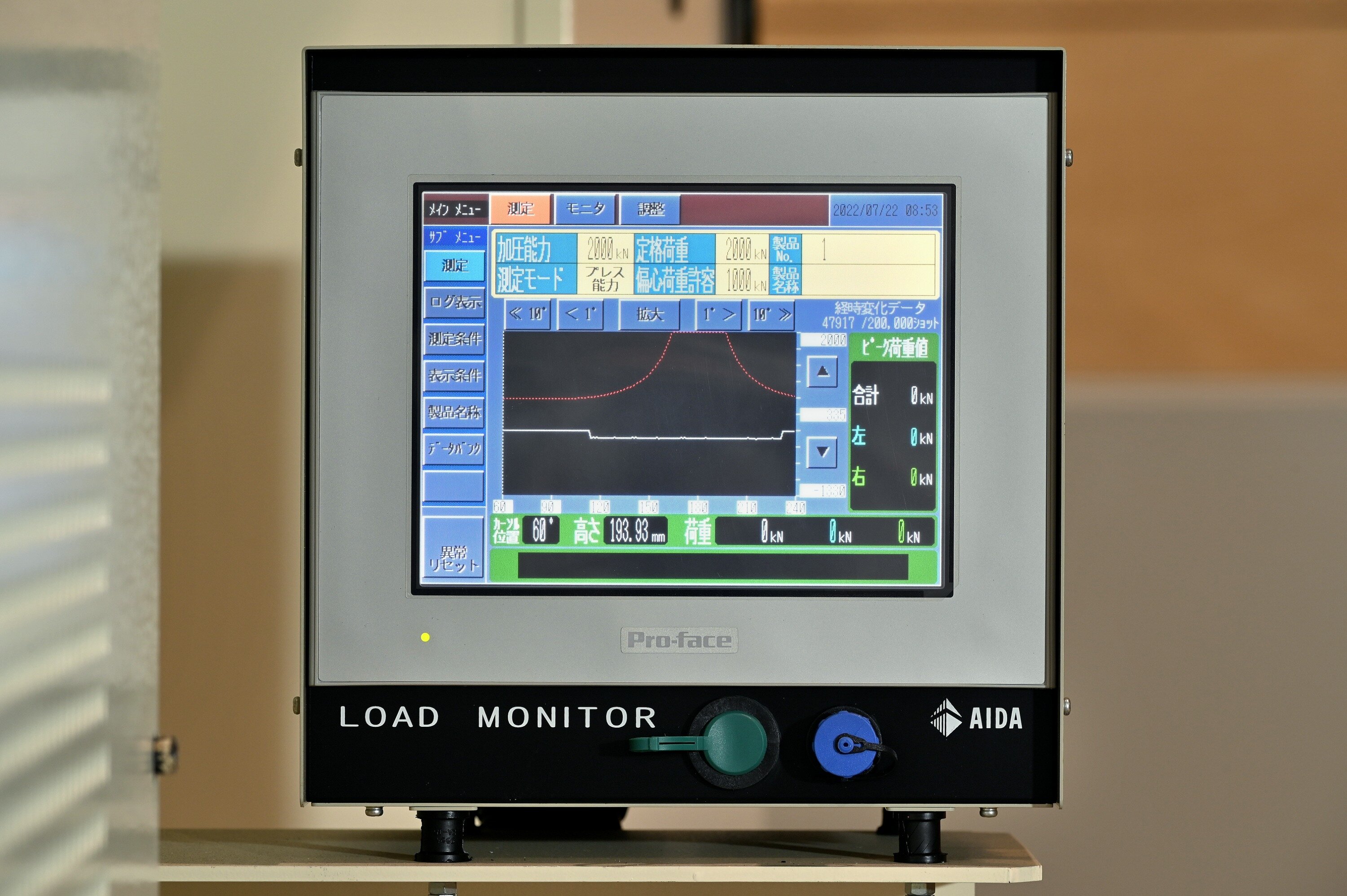
Draw-Forming (Part 3): How to Determine the Optimal Press Capacity
In Parts 1 and 2 of this series, we discussed the 'wrinkling suppression force' necessary to suppress wrinkling and cracking when draw-forming and how to calculate the 'appropriate number of draws....
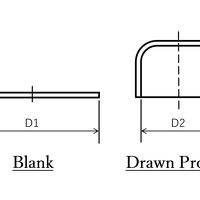
Draw-Forming (Part 2): How Do You Calculate the Appropriate Number of Draws?
In Part 1 of this series we discussed the 'wrinkling suppression force' necessary to suppress wrinkling and cracking when draw-forming. Draw-forming is a methodology that can produce seamless, beau...
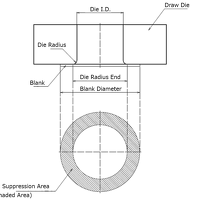
Draw-Forming (Part 1): How Do You Calculate the Optimal Wrinkling Suppression Force?
In this 3-part series we will be discussing 'draw-forming.' Drawforming is a methodology that can produce seamless, beautifully formed products, but it is very important to do calculations beforeha...
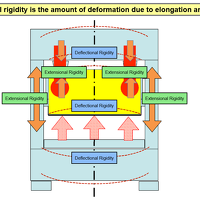
What is Press Rigidity?
When defects are found in press-formed products and other issues such as noise and vibration occur, you have perhaps heard someone comment, 'I don't think this press is rigid.' There are also diffe...
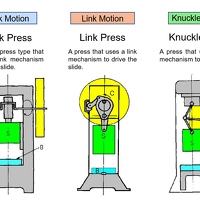
Different Types of Slide Motion and Their Torque Characteristics
There are many different slide motions available for mechanical presses, and this blog post will explain the characteristics of each motion, the slide drive mechanisms that make these motions possi...

Allowable Off-Center Load Diagrams--Part ②
In our previous blog post titled "Allowable Off-Center Load Diagrams--Part ①," we talked about cases where the load center is some distance from the center of the press (i.e., there is off-center l...

Frequently Asked Questions ~Metalworking Lubricants for Presses~
In this blog post, we will use a Q&A format to discuss frequently asked questions about metalworking lubricants. We also recommend this section for new learners! Q1: What are press metalworking...

What is the Total Press Weight? Understanding the Total Press Weight Applied on the Foundation
A press is a gentle yet powerful machine. A forging hammer is a type of machine that forms things in a way similar to a press. In the case of a hammer, the reactive force generated between the dies...

The 3 Elements of Press Capacity "Work Capacity"
Of the 3 elements of press capacity, so far we have explained "Pressure Capacity" and "Torque Capacity," so let's now talk about "Work Capacity." Work Capacity = The Amount of Energy Work capacity ...

shutterstock_153596720.jpg)